Blog
Populations at Risk: Understanding Cannabis Use Across Different Groups
Populations at Risk: Understanding Cannabis Use Across Different Groups
While cannabis has numerous potential benefits, it's important to recognize the unique risks it can pose to specific populations. Understanding these risks can help users make informed decisions and foster responsible cannabis use.
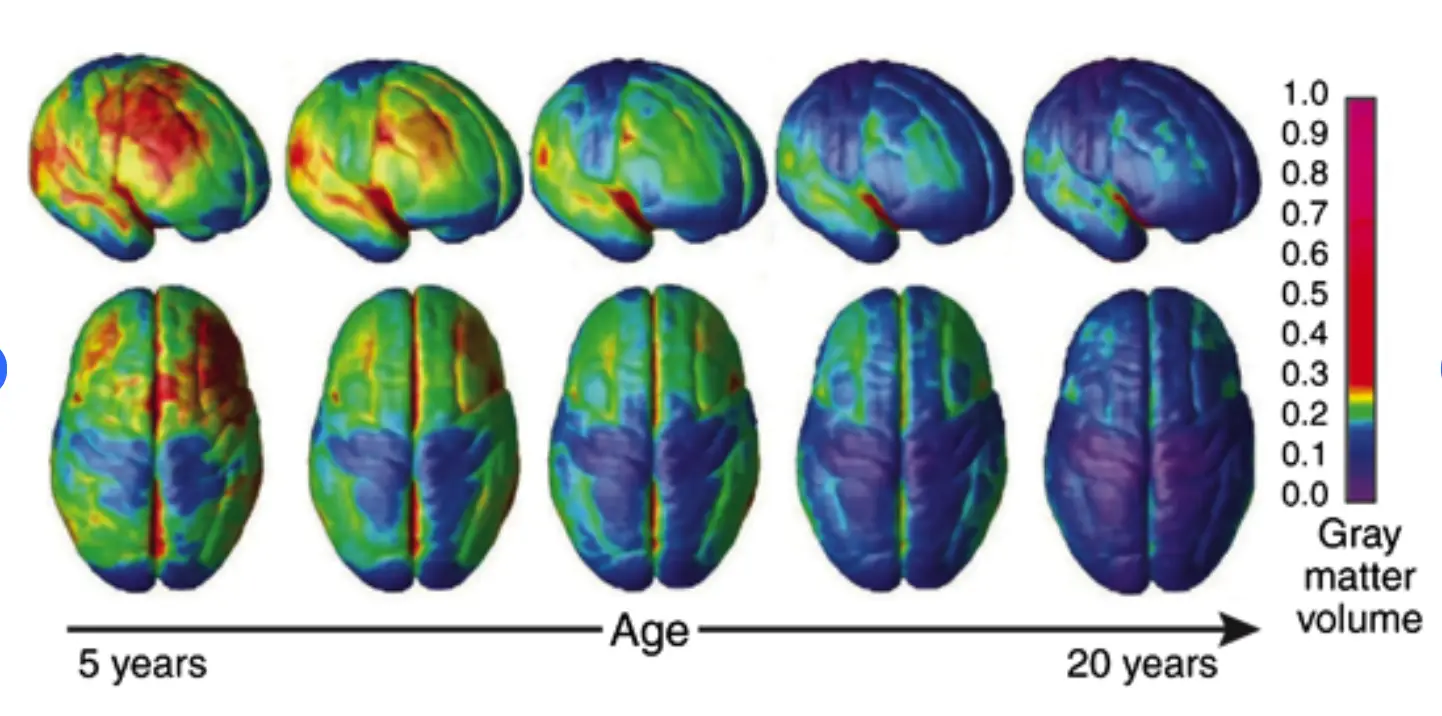
1. Adolescents and Young Adults
Did you know? The human brain takes 25 YEARS to fully develop! 🌱 From birth to early adulthood, our brains undergo incredible transformations. Making adolescents and young adults particularly vulnerable to the effects of cannabis.
- Risks: Impaired cognitive functioning, memory issues, reduced attention span, and increased likelihood of psychiatric conditions like anxiety and depression.
2. Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women
Cannabis use during pregnancy and breastfeeding poses risks to developing infants.
- During Pregnancy: Linked to low birth weight, developmental delays, and potential long-term cognitive and behavioral challenges.
- During Breastfeeding: THC can pass through breast milk, potentially affecting infant growth and development. (FUN FACT: Breast milk already contains endocannabinoids naturally produced by the body, which is why your baby looks high/drunk on milk as if they just had the ultimate milk happy hour 😄)

3. Older Adults
Older adults often face unique challenges with cannabis use due to slower drug metabolism and elimination.
- Risks: Increased susceptibility to dizziness, dry mouth, and other adverse reactions.
- Potential Benefits: If carefully monitored, cannabis can alleviate chronic pain, improve sleep, and enhance mood.
- Study Highlights:
- A 2017 Israeli study showed 93.7% of participants over 65 experienced symptom improvement after six months of cannabis use, with pain levels dropping from 8 to 4 on a 10-point scale.
- A Canadian study found that 72.7% of older adults reported reduced pain, 64.5% had better sleep, and 52.8% experienced mood improvements after 90 days of cannabis use.
- Study Highlights:

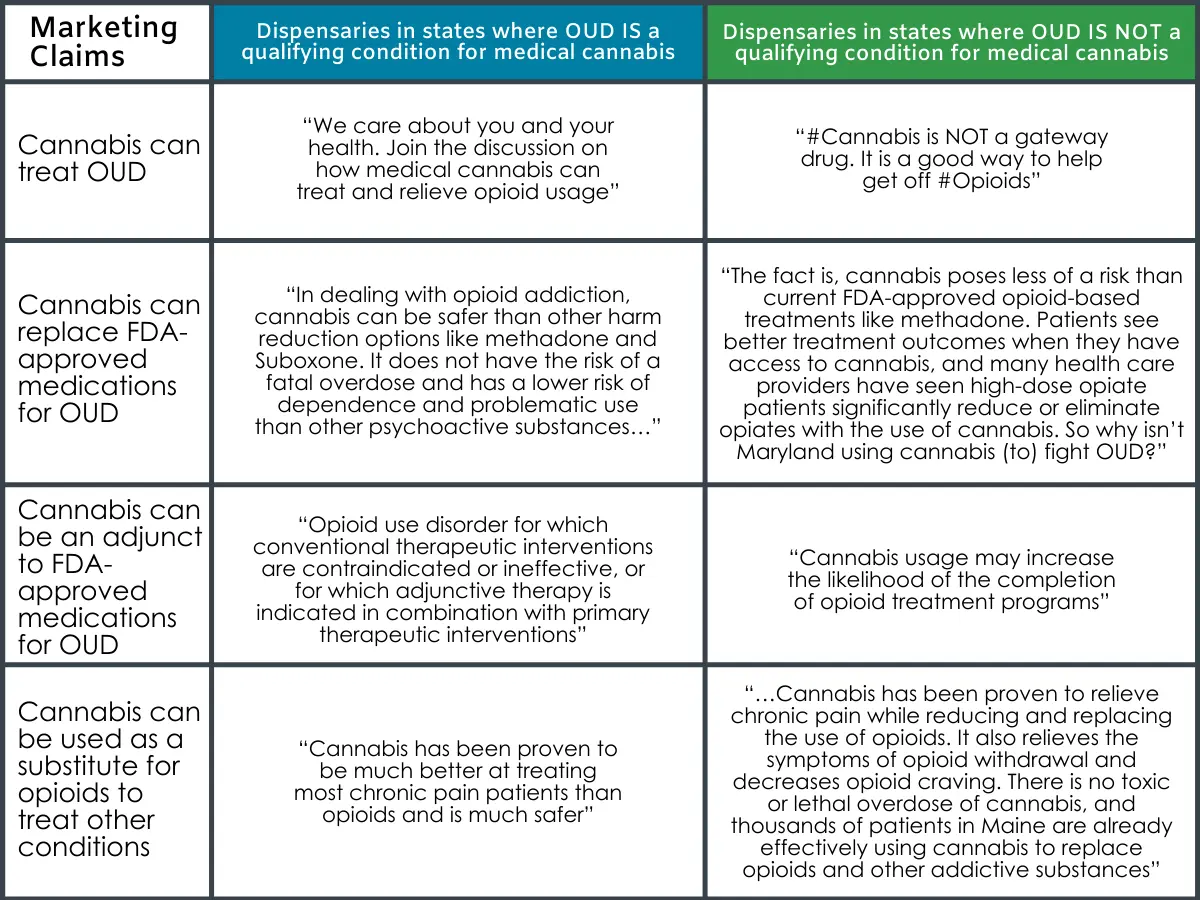
4. Individuals with Opioid Addiction
For individuals with a history of opioid addiction, there may be a higher risk of developing problematic cannabis use. However, early evidence suggests CBD might help manage Cannabis Use Disorder (CUD) and mitigate cravings.
Responsible Cannabis Use
It's essential for individuals, especially those in at-risk populations, to consult with healthcare providers before incorporating cannabis into their routine. Responsible use, tailored dosing, and understanding potential risks can lead to better outcomes.
Supporting Wellness Through Volaa
At Volaa, we believe in empowering our community with knowledge and products that prioritize wellness. Explore our collection, including:
- Keep Calm Tincture: Pure CBD to help with inflammation, nausea, and anxiety.
- Pain Relief Roll-On: Topical relief for localized pain and discomfort.
- Balance Gummies: Uplift your mood, regulate your ECS, and enjoy restful sleep when the time comes.
Browse Our Products Now
References:
Abuhasira, R., Bar-Lev Schleider, L., Mechoulam, R., & Novack, V. (2018). Epidemiological characteristics, safety and efficacy of medical cannabis in the elderly. European Journal of Internal Medicine, 49, 1-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2018.01.011
Backes, Michael. 2017. Cannabis Pharmacy. The Practical Guide to Medical Marijuana. Black
Dog and Leventhal Publishers.
Children’s Brain Tumor Foundation. 2024. https://www.instagram.com/cbtf_org/p/C2Aegslu66O/
Shover, C. L., Vest, N. A., Chen, D., Stueber, A., Falasinnu, T. O., Hah, J. M., … & Humphreys, K. (2020). Association of state policies allowing medical cannabis for opioid use disorder with dispensary marketing for this indication. JAMA Network Open, 3(7), e2010001. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.10001
Tau, Gregory & Peterson, Bradley. (2009). Normal Development of Brain Circuits. Neuropsychopharmacology : official publication of the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology. 35. 147-68. 10.1038/npp.2009.115.
Tumati, S., Lanctôt, K. L., Wang, R., Li, A., Davis, A., & Herrmann, N. (2022). Medical Cannabis Use Among Older Adults in Canada: Self-Reported Data on Types and Amount Used, and Perceived Effects. Drugs & aging, 39(2), 153–163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40266-021-00913-y
